An example from Optimal Multiple Importance Sampling Eq. 16
The original equation:
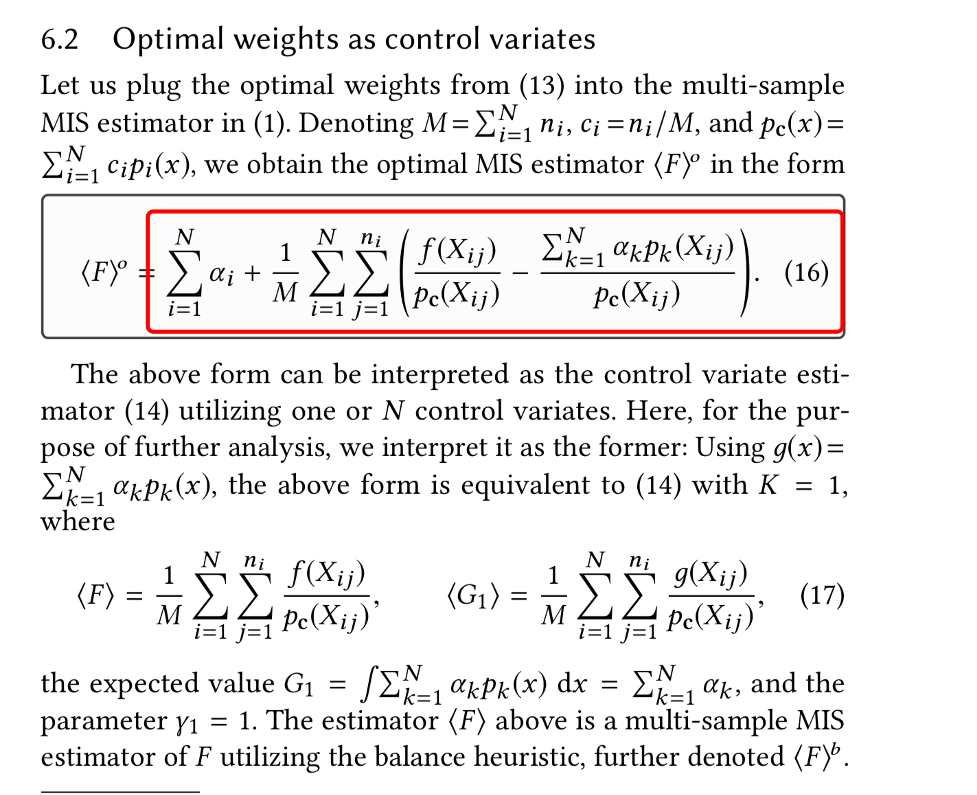
I❤️LA implementation:
∑_i α_i + 1/M ∑_i ∑_j (f(X_i,j)/`p_c`(X_i,j) - (∑_k α_k p_k(X_i,j))/`p_c`(X_i,j))
where
α ∈ ℝ^N
p_j ∈ ℝ → ℝ
X_i ∈ ℝ^(n_i)
M ∈ ℝ
f: ℝ → ℝ
`p_c`: ℝ → ℝI❤️LA compiled to C++/Eigen:
/*
∑_i α_i + 1/M ∑_i ∑_j (f(X_i,j)/`p_c`(X_i,j) - (∑_k α_k p_k(X_i,j))/`p_c`(X_i,j))
where
α ∈ ℝ^N
p_j ∈ ℝ → ℝ
X_i ∈ ℝ^(n_i)
M ∈ ℝ
f: ℝ → ℝ
`p_c`: ℝ → ℝ
*/
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <Eigen/Sparse>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
struct optimal_sampling_16ResultType {
double ret;
optimal_sampling_16ResultType(const double & ret)
: ret(ret)
{}
};
/**
* optimal_sampling_16
*
* @param f ℝ → ℝ
* @param p_c ℝ → ℝ
* @return ret
*/
optimal_sampling_16ResultType optimal_sampling_16(
const Eigen::VectorXd & α,
const std::vector<std::function<double(double)>> & p,
const std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> & X,
const double & M,
const std::function<double(double)> & f,
const std::function<double(double)> & p_c)
{
const long N = α.size();
const long dim_0 = X.size();
const long dim_1 = p.size();
assert( N == dim_1 );
double sum_0 = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=α.size(); i++){
sum_0 += α[i-1];
}
double sum_1 = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=X.size(); i++){
double sum_2 = 0;
for(int j=1; j<=X.at(i-1).rows(); j++){
double sum_3 = 0;
for(int k=1; k<=α.size(); k++){
sum_3 += α[k-1] * p.at(k-1)(X.at(i-1)[j-1]);
}
sum_2 += (f(X.at(i-1)[j-1]) / double(p_c(X.at(i-1)[j-1])) - (sum_3) / double(p_c(X.at(i-1)[j-1])));
}
sum_1 += sum_2;
}
double ret = sum_0 + 1 / double(M) * sum_1;
return optimal_sampling_16ResultType(ret);
}
void generateRandomData(Eigen::VectorXd & α,
std::vector<std::function<double(double)>> & p,
std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> & X,
double & M,
std::function<double(double)> & f,
std::function<double(double)> & p_c)
{
M = rand() % 10;
const int N = rand()%10;
const int dim_1 = N;
const int dim_0 = rand()%10;
α = Eigen::VectorXd::Random(N);
p.resize(dim_1);
for(int i=0; i<dim_1; i++){
p[i] = [](double)->double{
return rand() % 10;
};
}
X.resize(dim_0);
for(int i=0; i<dim_0; i++){
X[i] = Eigen::VectorXd::Random(rand()%10);
}
f = [](double)->double{
return rand() % 10;
};
p_c = [](double)->double{
return rand() % 10;
};
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
srand((int)time(NULL));
Eigen::VectorXd α;
std::vector<std::function<double(double)>> p;
std::vector<Eigen::VectorXd> X;
double M;
std::function<double(double)> f;
std::function<double(double)> p_c;
generateRandomData(α, p, X, M, f, p_c);
optimal_sampling_16ResultType func_value = optimal_sampling_16(α, p, X, M, f, p_c);
std::cout<<"return value:\n"<<func_value.ret<<std::endl;
return 0;
}I❤️LA compiled to Python/NumPy/SciPy:
"""
∑_i α_i + 1/M ∑_i ∑_j (f(X_i,j)/`p_c`(X_i,j) - (∑_k α_k p_k(X_i,j))/`p_c`(X_i,j))
where
α ∈ ℝ^N
p_j ∈ ℝ → ℝ
X_i ∈ ℝ^(n_i)
M ∈ ℝ
f: ℝ → ℝ
`p_c`: ℝ → ℝ
"""
import numpy as np
import scipy
import scipy.linalg
from scipy import sparse
from scipy.integrate import quad
from scipy.optimize import minimize
class optimal_sampling_16ResultType:
def __init__( self, ret):
self.ret = ret
def optimal_sampling_16(α, p, X, M, f, p_c):
"""
:param :f : ℝ → ℝ
:param :p_c : ℝ → ℝ
"""
α = np.asarray(α, dtype=np.float64)
X = np.asarray(X)
N = α.shape[0]
dim_0 = X.shape[0]
dim_1 = p.shape[0]
assert α.shape == (N,)
assert np.ndim(M) == 0
assert N == dim_1
sum_0 = 0
for i in range(1, len(α)+1):
sum_0 += α[i-1]
sum_1 = 0
for i in range(1, len(X)+1):
sum_2 = 0
for j in range(1, X[i-1].shape[0]+1):
sum_3 = 0
for k in range(1, len(α)+1):
sum_3 += α[k-1] * p[k-1](X[i-1][j-1])
sum_2 += (f(X[i-1][j-1]) / p_c(X[i-1][j-1]) - (sum_3) / p_c(X[i-1][j-1]))
sum_1 += sum_2
ret = sum_0 + 1 / M * sum_1
return optimal_sampling_16ResultType(ret)
def generateRandomData():
M = np.random.randn()
N = np.random.randint(10)
dim_1 = N
dim_0 = np.random.randint(10)
α = np.random.randn(N)
p = []
for i in range(dim_1):
def p_f(p0):
return np.random.randn()
p.append(p_f)
p = np.asarray(p)
X = []
for i in range(dim_0):
X.append(np.random.randn(np.random.randint(10)))
def f(p0):
return np.random.randn()
def p_c(p0):
return np.random.randn()
return α, p, X, M, f, p_c
if __name__ == '__main__':
α, p, X, M, f, p_c = generateRandomData()
print("α:", α)
print("p:", p)
print("X:", X)
print("M:", M)
print("f:", f)
print("p_c:", p_c)
func_value = optimal_sampling_16(α, p, X, M, f, p_c)
print("return value: ", func_value.ret)I❤️LA compiled to MATLAB:
function output = optimal_sampling_16(alpha, p, X, M, f, p_c)
% output = optimal_sampling_16(α, p, X, M, f, `p_c`)
%
% ∑_i α_i + 1/M ∑_i ∑_j (f(X_i,j)/`p_c`(X_i,j) - (∑_k α_k p_k(X_i,j))/`p_c`(X_i,j))
%
% where
%
% α ∈ ℝ^N
% p_j ∈ ℝ → ℝ
% X_i ∈ ℝ^(n_i)
% M ∈ ℝ
% f: ℝ → ℝ
% `p_c`: ℝ → ℝ
if nargin==0
warning('generating random input data');
[alpha, p, X, M, f, p_c] = generateRandomData();
end
function [alpha, p, X, M, f, p_c] = generateRandomData()
M = randn();
N = randi(10);
dim_1 = N;
dim_0 = randi(10);
alpha = randn(N,1);
p = {};
for i = 1:dim_1
p_f = @(p0) randn();
p{end+1,1} = p_f;
end
X = {};
for i = 1:dim_0
X = [X; randn(randi(10))];
end
f = @fFunc;
rseed = randi(2^32);
function tmp = fFunc(p0)
rng(rseed);
tmp = randn();
end
p_c = @p_cFunc;
rseed = randi(2^32);
function tmp = p_cFunc(p0)
rng(rseed);
tmp = randn();
end
end
alpha = reshape(alpha,[],1);
N = size(alpha, 1);
dim_0 = size(X, 1);
dim_1 = size(p, 1);
assert( numel(alpha) == N );
assert(numel(M) == 1);
assert( N == dim_1 );
sum_0 = 0;
for i = 1:size(alpha,1)
sum_0 = sum_0 + alpha(i);
end
sum_1 = 0;
for i = 1:size(X, 1)
sum_2 = 0;
for j = 1:size(X{i}, 1)
sum_3 = 0;
for k = 1:size(alpha,1)
sum_3 = sum_3 + alpha(k) * p{k}(X{i}(j));
end
sum_2 = sum_2 + (f(X{i}(j)) / p_c(X{i}(j)) - (sum_3) / p_c(X{i}(j)));
end
sum_1 = sum_1 + sum_2;
end
ret = sum_0 + 1 / M * sum_1;
output.ret = ret;
end
I❤️LA compiled to LaTeX:
\documentclass[12pt]{article}
\usepackage{mathdots}
\usepackage[bb=boondox]{mathalfa}
\usepackage{mathtools}
\usepackage{amssymb}
\usepackage{libertine}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{arg\,max}
\DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{arg\,min}
\usepackage[paperheight=8in,paperwidth=4in,margin=.3in,heightrounded]{geometry}
\let\originalleft\left
\let\originalright\right
\renewcommand{\left}{\mathopen{}\mathclose\bgroup\originalleft}
\renewcommand{\right}{\aftergroup\egroup\originalright}
\begin{document}
\begin{center}
\resizebox{\textwidth}{!}
{
\begin{minipage}[c]{\textwidth}
\begin{align*}
\omit \span \sum_\mathit{i} \mathit{α}_{ \mathit{i} } + \frac{1}{\mathit{M}}\sum_\mathit{i} \sum_\mathit{j} \left( \frac{\mathit{f}\left( \mathit{X}_{ \mathit{i}, \mathit{j} } \right)}{\textit{p\_c}\left( \mathit{X}_{ \mathit{i}, \mathit{j} } \right)} - \frac{\sum_\mathit{k} \mathit{α}_{ \mathit{k} }\mathit{p}_{ \mathit{k} }\left( \mathit{X}_{ \mathit{i}, \mathit{j} } \right)}{\textit{p\_c}\left( \mathit{X}_{ \mathit{i}, \mathit{j} } \right)} \right) \\
\intertext{where}
\mathit{α} & \in \mathbb{R}^{ \mathit{N}} \\
\mathit{p}_{\mathit{j}} & \in \mathbb{R}\rightarrow \mathbb{R} \\
\mathit{X}_{\mathit{i}} & \in \mathbb{R}^{ \mathit{n}_{\mathit{i}}} \\
\mathit{M} & \in \mathbb{R} \\
\mathit{f} & \in \mathbb{R}\rightarrow \mathbb{R} \\
\textit{p\_c} & \in \mathbb{R}\rightarrow \mathbb{R} \\
\\
\end{align*}
\end{minipage}
}
\end{center}
\end{document}
I❤️LA LaTeX output: